Botanical name: Sorghum vulgare [Pers]
Origin: East Central Africa, In India, it has been grown from pre-historic times
Family: Gramineae
Sorghum vulgare is one of the most important fodder crops of low rainfall areas of India. It can withstand heat and drought to a much greater extent than maize. Its other advantage is that it can give 2 to 3 ratoon crops and sometimes even four as in the case of M. P. Chari and Pioneer hybrid X-988. It can also tolerate water logging for short periods better than maize.
Soil : Well-drained sandy loams, Goradu and medium black soils are preferable.
Field preparation
The land should be prepared by two ploughing follows by harrowing and planking. The crop itself being shallow rooted does not require deep ploughing.
Sowing time
Kharif - June-July just after receiving first monsoon rain. In summer season, first or second week of March is most suitable.
Method of sowing
Drilling is the most common method. Seed can also be sown by iron funnel with a tube fixed behind a Desi plough to a depth not more than 3 to 4 cm. During the rainy season, seeds can be broadcasted at a little higher seed rate and mixed in soil with Desi ploughs or harrows.
Seed rate
60 kg for improved varieties
30 kg/ha for hybrids
Seed treatment
Seeds should be treated with 200 mess sulphur @ 4 to 5 g/kg of seeds for preventing measures against the grain smut disease. Andogonus Azotobacter culture @ 5 g or 5 ml is mixed with boiled Gur when it is cooled down and then it is used for seed treatment. Keep double rate of culture when seeds are treated with sulphur.
Spacing : Drilling at 25 to 30 cm apart.

Irrigation
Kharif sorghum does not require irrigation but for summer sorghum, apply irrigations at an interval of 10 to 15 days. Single cut system crop requires 4 to 5 irrigations whereas in two cutting system, the crop requires 7 to 8 irrigations.
Weeding
One interculturing operation is required after 15 to 20 DAS. Hand weeding is done after 30 to 35 DAS.
Harvesting
Forage sorghum varieties are harvested at the time of flowering stage; their forage is not harmful to the animals because at that stage (i.e. at 50 days after sowing) the concentration of HCN is below the poisonous limit, which is not harmful to the animal. At milking stage, HCN content is higher so, it is harmful to the small calf of cow and buffalo are not recommended to feed.
Maximum nutrients could be obtained by harvesting the crop at the time of flowering stage. The crude fiber content will be increased, while delaying the cutting will decrease the digestibility of nutrients and crude protein.
In two cutting system, first cutting should be done after two month of sowing and subsequent cuts would be harvested after 40 days of the first cut, as there is a possibility of adverse effect of fungicide/pesticide on animal. Therefore, the spraying of the same is not advisable at least one month before harvest.
Yield
In single cut system, green forage yield 350-400 q/ha. In two cut system, green forage yield 650 q/ha. In multi cut system, green forage yield 1100 to 1200 q/ha.
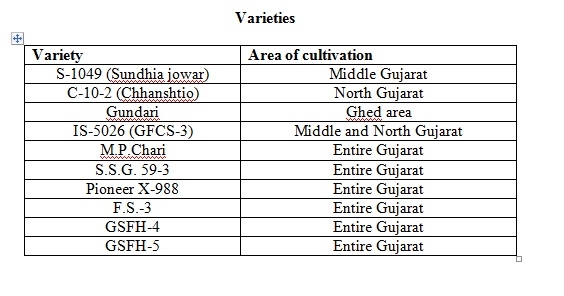
Research Station
Main : Main Forage Research Station, Anand and Surat.
Sub : Sub Research Station – Dhari (A,mareli), Navsari,
Chharodi.

