Major soils of India
----------------------------
1 Alluvial soil or Indo-gangetic Alluvium (Chemically it is Entisol)
1. These soils include deltaic alluvium, calcareous alluvium and coastal alluvium.
2. Alluvial soils are formed by transportation in streams and rivers and are deposited in flood plains or along the coastal belts.
3. They occur in the basins of Indus, Ganges, Brahmaputra, Godavari, Krishna, Cauvery and Tambiraparani deltas.
4. Alluvial soils of high altitude are acidic in nature and plains are neutral to alkaline.
5. Alluvial soils of plains are medium in phosphorous content and high in potassium content.
6. This is the most extensive soil found in India.
7. Out of total area of India, 48.0 m.ha comes under river alluvium.
8. Found in U.P., Bihar, West Bengal, Gujarat, Punjab, Rajasthan, AP, TN.
9. Many crops including vegetable is cultivated in river alluvium. Crops like rice, wheat, cotton, maize, sugarcane, vegetables, jute, oil seeds, millets, pulses and fruits are cultivated.
2 Black Soil
1. Dark-grey in colour due to clay-humus complex.
2. Area around 32.0 m.ha is under this soil.
3. It is chemically called as vertisol and derived from deccan basalt trap, granite and gneiss rocks.
4. This soil is also called black cotton soil, mixing of soil along the entire column with Montmorillonite clay.
5. Found in Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh,, South Orissa, South and Coastal Andhra Pradesh, North Karnataka and parts of Tamil Nadu.
6. Black soil contains high proportion of clay from 30 – 40%. So the water holding capacity is high.
7. Typical characteristics of this black soil are swelling (during wet period) and shrinkage (dry period).
8. Only after secondary tillage the soil is suited for crop production. The soils are dark in colour, fine grained contain high proportion of Calcium and Magnesium carbonates.
9. They are poor in N, medium in P and medium to high in K( Characteristic feature of typical Indian soil).
10. The soils are rich in montmorillonite and ellite type of clay with more cation exchange capacity (CEC) (40-60 m.e/100 g).
11. Crops grown in this soil are cotton, bengal gram, mustard, millets, pulses, oil seeds (sunflower, safflower) are commonly grown in this soil.
3 Red Soil (Alfisol)
1. Based on the colour (due to presence of ferric oxides) it is called as red soil.
2. They are formed from granites and other metamorphic rocks.
3. Mostly found in semi-arid areas and the colour varies from red to yellow.
4. Around 30 m.ha area found in India.
5. The soil is light textured, with kaolinite type of clay.
6. Well drained with moderate permeability.
7. Low cation exchange capacity and low water holding capacity.
8. Red soil is present in Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, North and East of Arunachal Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Parts of Bihar and Uttar Pradesh.
9. They are shallow in depth because they are degraded or drained soil. Less clay and more sandy than vertisol.
10. Red soil is always in acidic nature.
11. Highly suitable for groundnut crop cultivation.
12. Crops like millets, pulses, oil seeds (ground nut, gingerly, castor) and tuber crops like cassava are commonly cultivated.
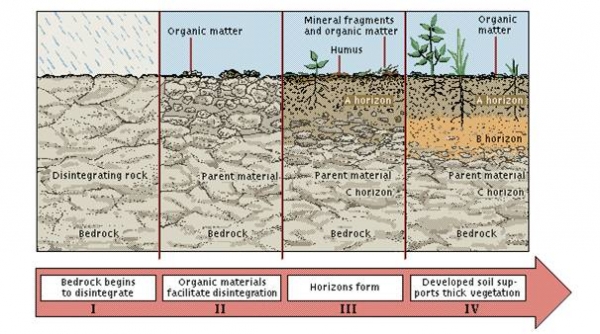
4 Laterites and Lateritic Soil
1. Laterite soil are formed due to the process of laterisation. i.e., leaching of all cations leaving Fe and Al oxides.
2. Mostly found in hills and foothill areas. Around 8 m.ha is covered with this oil.
3. This soil is formed under high intensive down pour of rainfall.
4. It is modified form of red soil, clay content is minimum.
5. Rich in fertility and medium water holding capacity.
6. They become very hard when there is no water.
7. Rich in organic matter content.
8. The cohesive nature is high.
9. Acid loving crops (Plantation crops) and fruits (pineapple, avacado) are more cultivated.
10. Tea, Rubber, pepper, spices are cultivated. At lower elevation places rice is grown.
5 Desert Soil
1. Found in desert regions of Rajasthan (Thar desert), parts of Haryana and Punjab.
2. More sand is found and sand dunes are common.
3. Poor fertility, poor water holding capacity and susceptible to soil erosion.
4. Clay content is < 8% only.
5. Presence of sodic salts (high Na content) leads to alkalinity.
6. Crops like date palm, cucumber, millets are cultivated (countries like Saudi Arabia, UAE, Jordan, Sudan etc).
6 Peaty and Organic Soil
1. These soils are very rich in organic matter.
2. Found in Kerala, coastal regions of West Bengal, Orissa, South and East coast of Tamil Nadu.
3. Deposition of organic matter by the elevated soil.
4. Peaty and organic soil is not suitable for majority of crops.
5. Rice is mostly cultivated in coastal area in rainy season.
Lateritic soil formation
Different types of soils of India

