Microeconomics:
----------------
Micro means small. Thus, micro economics analyses individualistic behaviour. It studies an individual consumer, producer, price of a particular commodity, household, etc.
According to Prof. K. E. Boulding, "Micro Economics is the study of particular firm, particular household, individual prices, wages, incomes, individual industries and particular commodities."
Study of Economics:
-------------------
The study of economics is divided by the modern economists into two parts viz. Micro economics and Macro economics.
Micro economics and Macro economics, both the terms were used in 1933 by Prof. Ragnar Frisch from Oslo University of Norway.
The word micro has been derived from the Greek word `Mikros` i.e. small and the word macro has been derived from Greek word `Makros` i.e. large.

Subject Matter or Scope of Microeconomics:
------------------------------------------
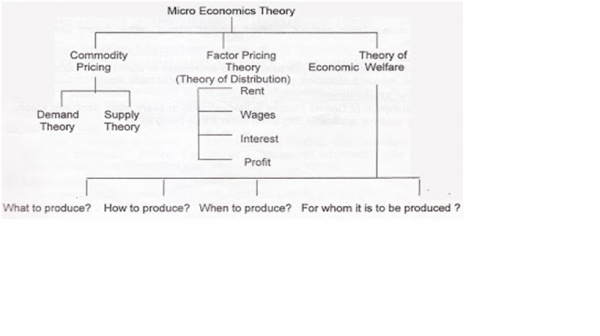
1. Commodity Pricing:
-------------------------
Prices of individual commodities are determined by market forces of demand and supply. So micro economics makes demand analysis (individual consumer behaviour) and supply analysis (individual producer behaviour).
2. Factor Pricing:
-------------------
Land, labour, capital and entrepreneur, all factors contribute in production process. So they get rewards in the form of rent, wages, interest and profit respectively. Micro economics deals with determination of such rewards i.e. factor prices. So micro economics is also called as `Price Theory` or `Value Theory`.
3. Welfare Theory:
------------------
Micro economics deals with optimum allocation of available resources and maximisation of social welfare. It provides answers for `What to produce?`, `When to produce?`, `How to produce?` and `For whom it is to be produced?`. In short, Micro economics guides for utilizing scarce resources of economy to maximize public welfare.

