What is Economics?
-------------------
If we see our day-to-day activities, most of which are related to earning one`s own living and to the manner of satisfying one`s own wants. These human activities, which are generally called economic, are mainly related to production, distribution, consumption and exchange of goods and services. The scientific study of various problems arising out of these economic activities is called economics.
Concept of Economics:
--------------------
The word economics has been derived from the Greek word “OIKONOMICAS” with “OIKOS” meaning a household and “NOMOS” meaning management. It is understood that the beginning was made by the Greek Philosopher, Aristotle who in his book “Economica” focused that the field of economics deals with household management.
1. Wealth
2. Welfare
3. Scarcity and
4. Growth.
Chronologically Development of Economics:
-----------------------------------------
1. Wealth:
-----------

Adam Smith (1723-90)
In his book entitled “Wealth of Nations”(1776) defined economics as “An enquiry into the nature and causes of the of wealth of nations”. He is known as the “Father of Economics” because he was the first person who put all the economic ideas in a systematic way.
2. Welfare:
-------------

Alfred Marshall (1842-1924)
In his a book Principles of Economics in 1890. According to him “Economics is a study of man`s actions in the ordinary business of life; it inquires how he gets his income and how he uses it”.
3. Scarcity:
-------------

Lionel Robbins (1898-1984)
Robbins has given the above definition in his book “An Essay on the Nature and significance of Economic Science”. “Economics is the science which studies human behaviour as a relationship between ends and scarce means which have alternative uses”.
4. Growth:
------------

Lord Keynes (1883-1946).
Economics as “the study of the administration of scare resources and of the determinants of employment and income”. Thus, besides studying the resource allocation, Economics studies how the levels of income and employment in an economy are determined.
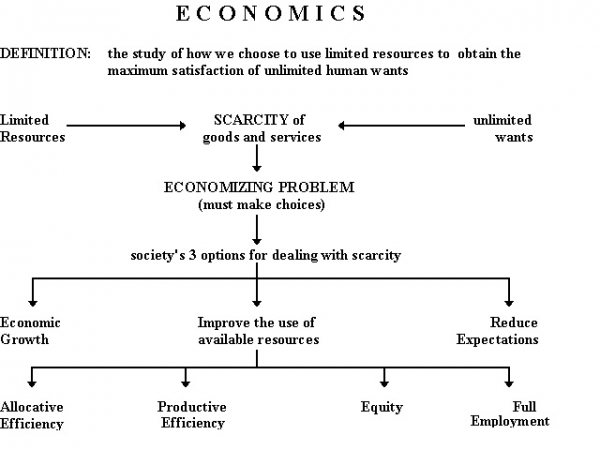
Basic Economic Problem (Alternate use of Resources):
--------------------------------------------------------