A. Feeding ewes in different stages
1. Feeding considerations for breeding ewes
Suggested flushing rations
--------------------------
• A good mixed pasture of legumes and grasses,
• A grass pasture plus 150 g of wheat bran per head per day,
• Grass pasture plus 250 g of grains and 450 g of oil cakes,
• Legume hay full fed plus 100 g of wheat bran and 150 to 200 g of grain and
• Green fodder at the rate of 10 per cent of body weight and 150-200 g of concentrate per head per day.
Rations for ewes during early and mid-pregnancy
-----------------------------------------------
• Grazing: On a good pasture. .
• Sorghum silage: One to two kg. Sorghum silage plus legume hay half to one kilogram per head per day.
• Ad libitum supply of maize or sorghum fodder plus 50g of oil cakes like groundnut cake, per head per day
• Grazing on stubbles and harvested fields supplemented with 100 g of oil cakes per head per day.
Feeding ewes during late pregnancy
---------------------------------
• Allowed to graze on crop aftermaths (crop stubbles), wild grasses and weed supplemented with available green fodder fed at the rate of 5 kg per head per day.
• Molasses or grains (barley, maize, oats, etc.) may be fed at the rate of 225 g /head/ day.
• Ewes should also receive available green fodder at the rate of 7 kg/ head /day or 600 g of quality legume hay or 300 g of concentrate with 12 to 14 % DCP and 65 to 70% TDN during last 45 days of pregnancy.
Feeding ewes at lambing time
----------------------------
• Bulky and laxative feedstuffs may be included in the ration during the first few days.
• A mixture of wheat bran and barely or oats or maize at 1: 1 proportion is excellent.
• As lambing time approaches or immediately after lambing, the grain allowance should be materially reduced but good quality dry roughage should be fed free choice.
Feeding lactating ewes
----------------------
• An average ewe`s daily pasture requirements can be replaced by 50 per cent by 450 g of good hay, 1.4 kg silage or 250 g of grain.
• If they are fed cultivated green fodder, 10 kg per head is sufficient or 400 g of concentrate mixture or 800 g of quality legume hay /day for 75 days after lambing in addition to 8 hours of grazing.
Feeding rams for breeding
-------------------------
• Allow the rams to graze with the ewes, which will allow the rams to get the same ration as the ewes.
• If separate feeding is practiced for the ram, it may be given 300-500 g of concentrate mixture consisting of three parts oats or barely, one part maize and one part wheat per day.
Feeding suckling lambs
----------------------
• Keep on its mother`s milk to a considerable degree for its nutrition.
• At one month of age the young ones should be provided with the concentrate mixture (Creep feed).
Colostrum feeding of lambs
--------------------------
• The lamb should be allowed to suck its dam for the first three or four days so that they can get good amount of colostrum to disowning by the mother.
• Colostrum is given @ 100 ml per kg live weight.
Creep feeding for lambs
-----------------------
• This creep feed may be started from one month of age and up to 2-3 months of age.
• The quantity to be given to the lambs is 50 – 100 gm/animal/day with 22% protein.
Composition of ideal creep feed
-------------------------------
• Maize - 40%
• Ground nut cake -30 %
• Wheat bran – 10 %
• Deoiled rice bran- 13 %
• Molasses – 5%
• Mineral mixture- 2%
• Salt – 1% fortified with vitamins A, B2 and D3 and antibiotic feed supplements
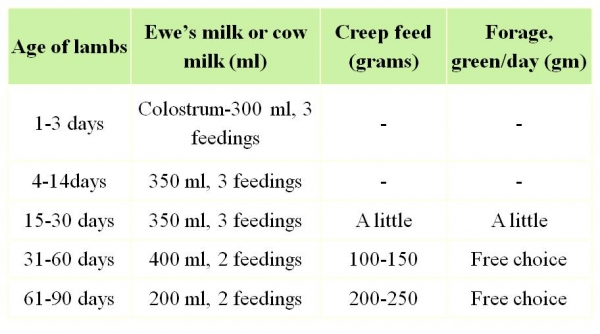
Feeding schedule for a kid/lamb from birth to 90 days:
Feeding from weaning to market
------------------------------
• Good quality fodder, hay or concentrates. .
• An average lamb may be fed 225 to 450g of concentrate mixture listed below depending on the grazing conditions.
• If there is plenty of grazing 225g is sufficient.
• In over-grazed grasslands they may be given 450g of the concentrate mixture plus half to two kilogram of good green fodder.
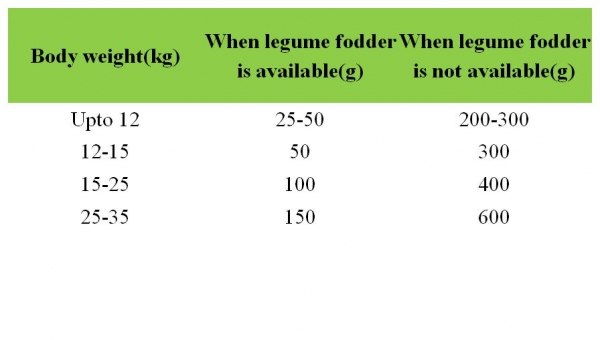
Rate of feeding concentrate per day