Synonyms:
----------
Bang`s disease, Undulant fever, Mediterranean fever
• An mportant Zoonotic disease
• Reproductive losses ® abortions, placentitis, epididymitis & orchitis - Animals.
• An agent of bio-terrorism
• Chronic bacterial disease
• a serious, debilitating, non –fatal ® a systemic disease ® human
ETIOLOGY:
--------
• - a Gram negative, non-motile, facultative intracellular, coccobacillary/ short rod shaped organism.
• Strict aerobes , fastidious - Blood agar
• Species specific
• Chlamidophila abortus & Coxiella brunette indistinguishable from Brucella
• B.abortus – frequent B.melitensis - Less frequent
• B.suis – Occasional B.ovis - sheep not goats
• B. abortus - Frequent - cattle, bison, buffalo & human – Nine biovars
• B. Melitensis, B.ovis -Less frequent - Sheep and goats – Three biovars
• B.suis - Occasional - Pigs – Reindeer, caribou & rodents - Five biovars
• B.canis -Dogs, human
• B.maris -Marine mammals , human
• B.pinnipdedialis -Pinnipeds - seals, sea lions & walruses
• B.cetaceae - Cetaceans - whales, porpoises & dolphins
PREVALENCE:
-----------
Clinical disease - Report - Middle East, Asia, Africa, South and Central America, the Mediterranean Basin & the Caribbean
B.abortus : Eradicated ® cattle - U.S, Japan, Canada, some European countries, Australia, New Zealand and Israel, but - wildlife - some region - North America
B. melitensis – Mediterranean, the Middle East, Central Asia, the Arabian Gulf, some countries of Central America, Africa & India ; It cross reacts with Yersinia enterocolitica 0:9.
B. ovis : Probable occurrence : Most sheep raising parts across the world
B.suis : Eradicated ® Domesticated pigs - U.S. Canada, many European countries.
• Sporadic outbreaks : human & pigs
• Biovar-4 - Rangiferine Brucellosis
• Biovar-5 -Murine Brucellosis - New Zealand & Australia - free from this organism
TRANSMISSION:
-------------
• Contact ® placenta, fetus, fetal fluids & vaginal discharges ® Infected anima
• Venereal spread – B.abortus - Cattle – not more common but for B. ovis. B. suis and B. canis - Frequent.
• Ingestion, mucous membranes, broken skin
• Lateral transmission - Fomites, feed & water
• From milkers & farmers hands
HOST AFFECTED:
--------------
• Cattle, bison, buffalo, sheep, goats, pigs, dogs, horses, camels – affected
• Sheep & goats -Reservoir - B.melitensis
• Deer -Maintenance host - B.ovis
• Wildlife reservoirs - feral pigs, bison, elk & European hares
• Pinnipeds & cetaceans - spread the infection
Sources of infection:
---------------------
• Following first time abortion - Cattle - Asymptomatic chronic carriers - Continue to shed organism - Milk & uterine discharges.
• Pregnant animals- Gravid uterus - harbor the organism
• Non-pregnant animals - Mammary gland - reservoir for organism
• Dogs - shed the organism - later stage of pregnancies
• Bull semen – for a longer period
• Urine, feces, hygroma fluids, saliva, nasal & ocular discharge
PATHOGENESIS:
------------
• Brucllosis ® Ingestion, inhalation & direct contact ® Food & other materials
• Upon entry -Phagocytosed by neutropils, monocytes, multiply & get localized ®Regional lymphnodes if not killed.
• Localization occurs mainly in organs rich in sugar, Erythritol - breast, uterus, epididymis.
• In phago-lysosome , the trapped organism releases 5` -guanosine & adenine which inhibits the degranulation of peroxidase-containing granules & again inhibit the myeloperoxidase-peroxide-halide system of phagocytic killing.
• Intracellular persistence ® Granuloma formation in organs & tissues - due to hypersensitivity reactions - Type-IV
• Later stage, distributed to ® Lymphoreticular organs ® Spleen, BM liver & testes where ® Granulomas / microabscesses ®Infected animals remain as carriers.
CLINICAL SIGNS:
--------------
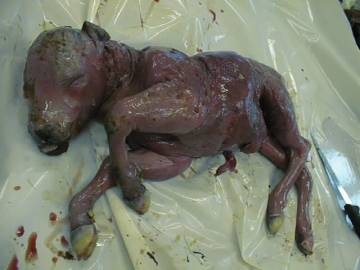
B.abortus : Cattle: Abortion – 2nd half ® Full term pregnancy – No abortion in subsequent pregnancy
Metritis, still births, weak offspring, RFM, infertility, repeat breeding
epididymitis, seminal vesiculitis, orchitis, testicular abscess, infertility
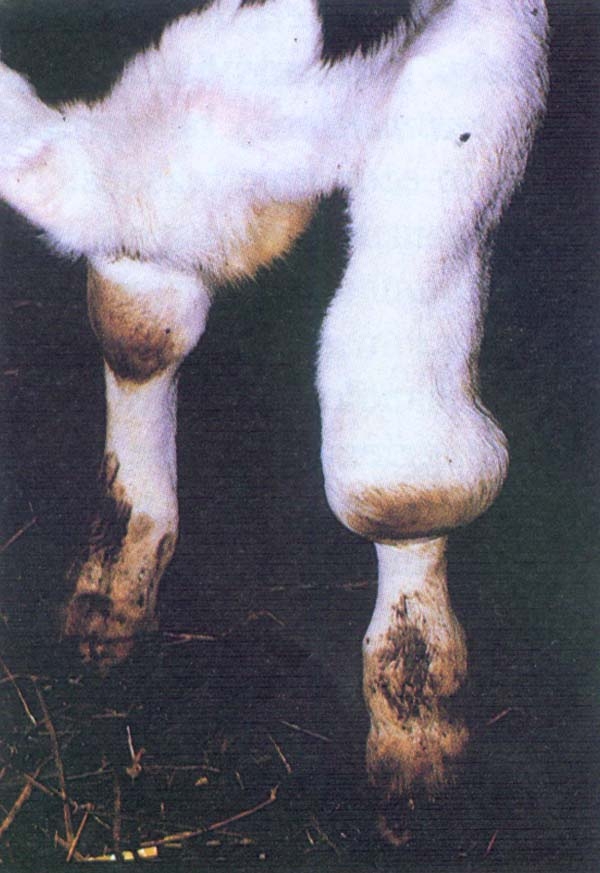
unilateral / bilateral hygroma & arthritis
Reduction in milk yield, mastitis - “Flabby bag syndrome”
Rarely causes fetal death
B.melitensis : Sheep & Goats: Abortions - 2ndwks ® 5th wks –Pregnancy
Reinvasion during subsequent pregnancies occurs
Other signs similar to cattle
B.ovis: sheep not goats. Epididymitis (unilateral occasionally bilateral),
Atrophied testes
B.suis: Pigs :Abortion - At any time of pregnancy
Temporary / permanent orchitis & sterility - common
Boars - persistent carriers.
Hares - Purulent nodules - internal organs, reproductive organs, subcutaneous tissues & muscles
Other signs similar to cattle
B.abortus: Horses: Abortion – rare
Inflammation of supra spinous / supra atlantal bursa ® “Fistulous withers” or “poll evil”
Bursal sacs ® Distended / thick wall, rupture ® secondary inflammation
Chronic cases: Necrosis of nearby ligaments / dorsal vertebral spines
B.canis:Dogs:
• Abortion - 7-9thwks pregnancy.
• a mucoid, serosanguineous / gray green vaginal discharge - persists for up to 6wks. Early embryonic death,
• Pups born alive become weak & develop disease
• Chronic infection: Scrotal edema , unilateral or bilateral testicular atrophy & lymphadenitis - common
• Disc-spondylitis - thoracic & lumbar vertebrae - stiffness, lameness, back pain, uveitis, endophtholmitis, polygranulomatous dermatitis, endocarditis, & meningoencephalitis
POST MORETEM LESIONS:
--------------------
• Autolysis of fetus, subcutaneous edema, vaginal discharge
• Inflammation of placenta & cotyledeons become red, yellow
• Inter cotyledonary parts - typically leathery with focal thickening & exudate
• Granulomatous to purulent lesion - mammary gland, superficial lymphnodes, lymphoid tissues
• Mild ® severe endometritis, unilateral / bilateral epididymitis / orchitis
• Hygroma of knee joint, fetlock, hock, stifles, haunch, nuchal ligaments and thoracic spines
• Hares - Purulent nodules
• Fibrous atrophy of testes
• Enlargement - retropharyngeal, inguinal LNs
• Scrotal edema, dermatitis, prostatitis,
ZOONOIS:
-------
• An occupational hazard.
• Accidental injection -
• Blood transfusion, bone marrow transplantation or sexual contact
• Congenital infection
• Crossing placental barrier & breast milk feeding ® fetal infection
IP - 5 days to three months
B. melitensis - the most severe human pathogen followed by B. abortus, B. suis & B.canis
Human infections - asymptomatic & self limiting
Slow recovery rate
Neurobrucellosis & spinal osteomyelitis
Meningitis & endocarditis
• .
CLINICAL SIGNS:
--------------
• Flu like signs - fever, head ache, malaise, back pain & muscular pain Drenching night sweats, cough & pleuritic chest pain
• Gastrointestinal signs - anorexia, nausea, vomition, diarrhoea & constipation
• Undulant fever - recover completely – 3-12 months ® Chronic illness
• Complication - arthritis, spondylitis, epididymo-orchitis, & chronic fatigue
• Endocarditis & meningitis ® death
• Systemic infection- nephritis, vasculitis, lymphadenopathy, granulomatous hepatitis, osteomyelitis
Congenitally infection : premature birth / born to full term ® low birth weight, fever, failure to thrive, jaundice, hepatomegaly & spleenomegaly - No spontaneous abortion
DIAGNOSIS:
---------
Stamp`s modified Ziehl Neelsen method: Coccobacilli or short rods, a single chain / pairs / small groups – resembles Coxiella burnetii
Isolation of organism : Blood & bone marrow - positive at this stage. Plain / selective media - Farrell`s media / Thayer-Martin`s modified & enriched media – culture
• B. abortus, B. suis, B. melitensis: smooth colonies with defined smooth margins. Colonies - translucent, pale honey colored & on top convex & pearly white.
• B. ovis & B. canis ® rough colonies, round, shiny & convex
• Serology: Coombs` test (antiglobulin)
SEROLOGY:
---------
Rose Bengal Plate Agglutination Test (RBPT)
Indirect Elisa : an international trade test
Brucellin Skin Test:
Serum Tube Agglutination Test (STAT):
an antibody test.
Milk Ring Test (MRT): Culture : Brucella colony
CONTROL:
---------
• B. abortus 19 & B. melitensis Rev-1 vaccine strain – Bio=safety containment level 3 / higher.
• 1% hypochlorite solutions, 70% ethanol, isopropanol, iodophores, phenolic disinfectants, formaldehyde, glutaraldehyde & xylene –killing
• 2.5% sodium hypochlorite, 2-3% caustic soda, 20% fresh slaked lime suspension, 2% formaldehyde solution - sprayv inactivating the organism
• Moist heat of 121°C for at least 15 minutes (autoclave) - Equipments.
• Dry heat for 160-170°C for at least 1 hour (Hot air oven)
• Xylene (1ml/liter) and calcium cyanamide (20 kg/m3) –Liquid -2-4wks
• Pasteurization
• Screening , culling & isolation
• Proper disposal of infected carcass/aborted fetus and placental membrane.
• Stamping out policy
VACCINE:
-------
B. abortus strain - 19 vaccine:
• prevention of brucellosis.
• a live vaccine ® Only to female calves of 3-6months -s/c - 5-8x1010 viable organisms
• adult cattle 3x108 organism is given s/c route - animals develop persistent antibody titers, abort & excrete the vaccine strain in milk.
Brucella abortus strain RB51 vaccine: from a laboratory derived rough mutant of smoonth B.abortus strain 2308.
• Calves - 4-12 months old vaccinated with 1-3.4x1010 viable strain RB51 organisms.
• Vaccination - cattle >12 months - with permission of Federal Animal Health Officials
• good immune response with booster dose
Brucella Melitensis strain Rev.1 vaccine:
• more effective in small ruminant