Wind mill or wind turbine:
--------------------------
Wind mill is a device for wind energy conversion. Wind turbine converts the energy of wind into kinetic energy and this mechanical energy then converted to electricity. This type machine can called a wind generator, wind turbine, wind powerunit (WPU), wind energy converter (WEC), or aero generator.
Types of wind mills:
Wind turbines can rotate about either a horizontal or vertical axis. Therefore, it is broadly divided into two groups:
1. Horizontal axis wind mills:
i. Single blade wind mills
ii. Double blade wind mills
iii. Multi blade wind mills
2. Vertical axis wind mills:
i. Savonius or S type wind mill (low wind velocity)
ii. Darrieus wind mill (high wind velocity)

Coastal Windmills
1. Horizontal axis wind mills:
These types of wind mills have main rotor shaft and electrical generator at the top of a tower and must be pointedinto the wind. Small turbines are pointed by a simple wind vane, while large turbines generally use a wind sensor coupled with a servo motor. Most have a gearbox, which turns the slow rotation of the blades into a quicker rotation that is more suitable to drive an electrical generator. Since a tower produces turbulence behind it, the turbine is usually pointed upwind of the tower.Turbine blades are made stiff to prevent the blades from being pushed into the tower by high winds. Additionally, the blades are placed a considerable distance in front of the tower and are sometimes tilted forward into the wind.

Horizontal Axis Wind Mills
i) Horizontal axis propeller type wind mill with single blade
In this type of machine, a long blade is mounted on a rigid hub. Induction generator and gear box are arranged as shown in figure 1. If extremely long blades (60 m) are mounted on the hub, large blade root bending moments may occur due to tower shadow, gravity and sudden shifts in the wind directions. To reduce rotor cost use of low cost counter weight is recommended for balancing long blade centrifugally.

Horizontal Axis Single Blade Wind Mill
ii) Horizontal axis - two blade wind mill
In this design rotor drives a generator through a step-up gear box. The blade rotor is designed to be oriented downwind of the tower. The components are mounted on a bedplate, which is attached on a pintle at the top of the tower.
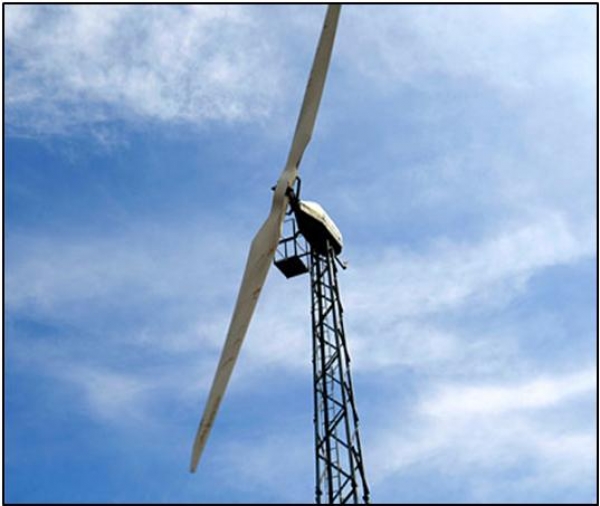

Horizontal Axis Double Blade Wind Mill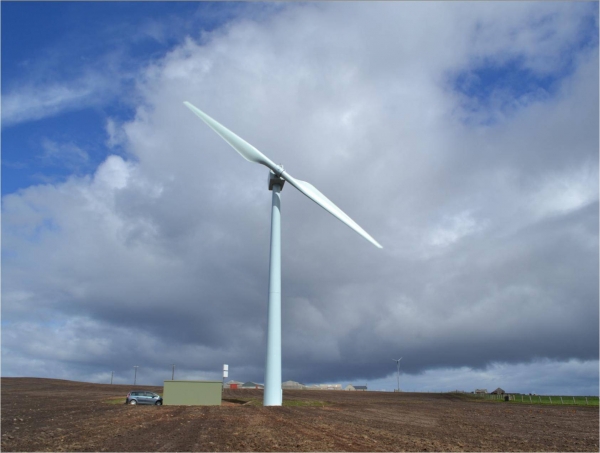
Horizontal Axis Double Blade Wind Mill
iii) Horizontal axis-multi blade type wind mill
This type of design for multi blades is shown in figure. Blades are made from sheet metal or aluminium. The rotors have high strength to weight ratios and are strong enough to with stand a wind speed of 60 Kmph. This type of wind mills have good power coefficient, high starting torque, simple and are low in cost.

Horizontal Axis Multi Blade Wind Mill
Horizontal Axis Multi Blade Wind Mill
2. Vertical axis wind mill:
They have the main rotor shaft arranged vertically. Key advantages of this arrangement are that the turbine does not need to be pointed into the wind to be effective. This is an advantage on sites where the wind direction is highly variable.With a vertical axis, the generator and gearbox can be placed near the ground, so the tower doesn’t need to support and it is more accessible for maintenance. Drawback is some designs produce pulsating torque.
It is difficult to mount vertical-axis turbines on towers, meaning they are often installed nearer to the base on which they rest, such as the ground or a building rooftop. The wind speed is slower at a lower altitude, so less wind energy is available for a given size turbine. Air flow near the ground and other objects can create turbulent flow, which can introduce issues of vibration, including noise and bearing wear which may increase the maintenance or shorten the service life. However, when aturbine is mounted on a rooftop the building generally redirects wind over the roof and this can double the wind speed at the turbine. If the height of the rooftop mounted turbine tower is approximately 50% of the building height, this is near the optimum for maximum wind energy and minimum wind turbulence.
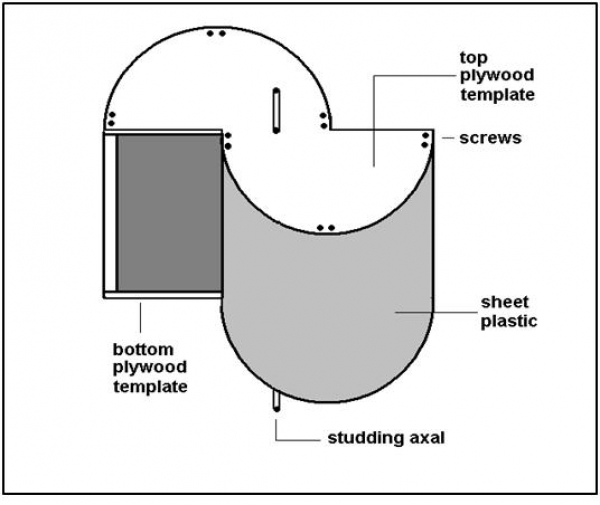
Diagram of Savonious Wind Mill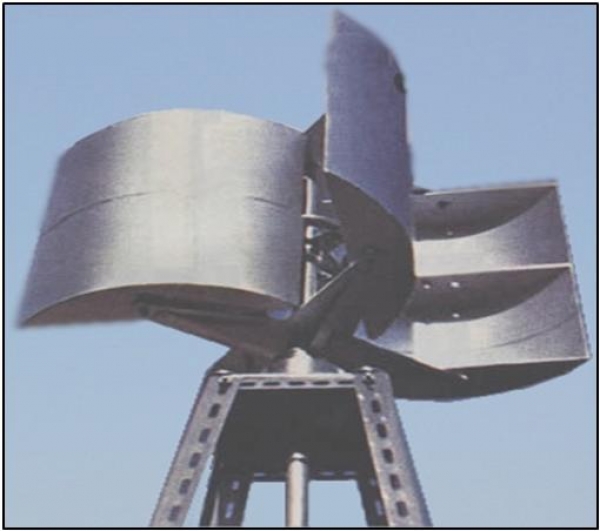
Savonious Wind Mill
i) Savonius Wind Mill
These are drag-type devices with two (or more) scoops that are used in anemometers, Flettner vents (commonly seen on bus and van roofs), and in some high-reliability low-efficiency power turbines. They are always self-starting if there are at least three scoops. Sometimes they have long helical scoops to give a smooth torque.
ii) Darrieus windmill
Darrieus turbine or “Eggbeater” turbines were named after the French inventor, GeorgesDarrieus. It has good efficiency, but produce large torque ripple and cyclical stress on the tower, which contributes to poor reliability. They also generally require some external powersource, or an additional savonius rotor to start turning, because the starting torque is very low.The torque ripple is reduced by using three or more blades which results in a higher solidity forthe rotor. Solidity is measured by blade area divided by the rotor area.
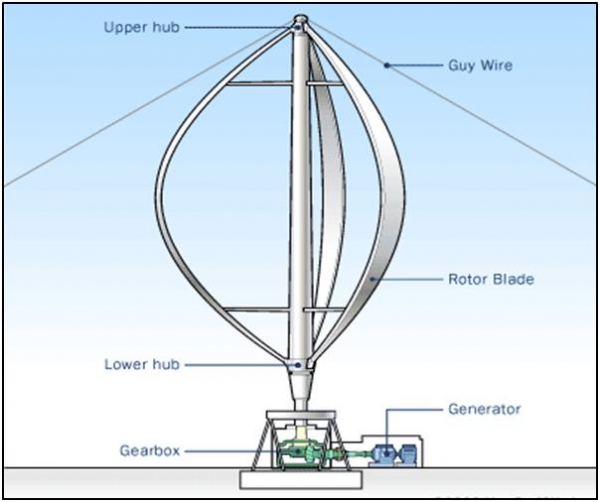
Derious Wind Mill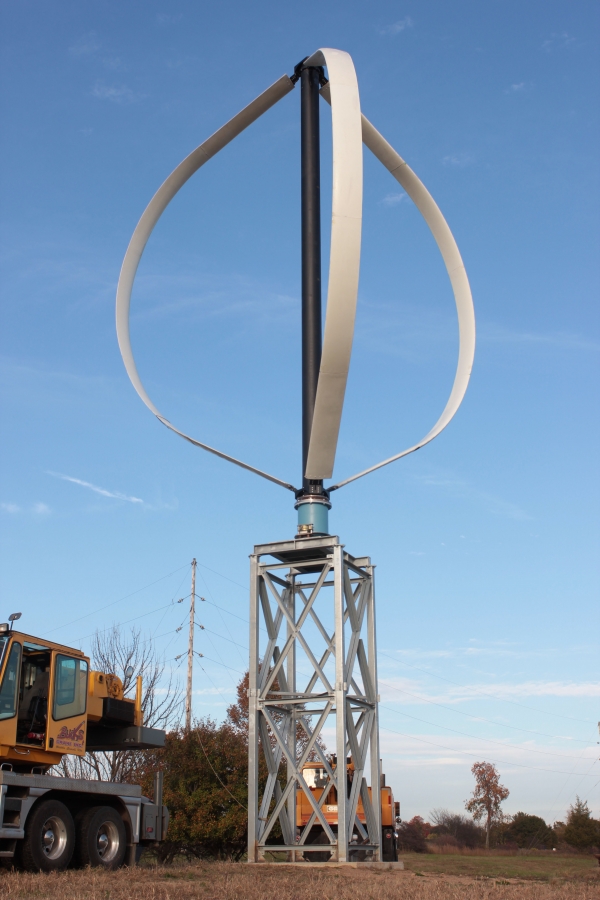
Derious Wind Mill

