Types of Cropping Systems
------------------------------
1. Sole cropping
Only a single crop or variety grown alone in a pure stand at normal density during one farming year.
2. Mono cropping/ mono culture
Continuous production of one and the same crop year after year or season after season is called mono cropping. It may be due to climatologically and socioeconomic conditions or due to specialization of a farmer in growing a particular crop.
3. Multiple/Intensive cropping
Growing two or more crops on the same piece of land in one calendar year is known as multiple cropping. It is used to intensify the production. It is possible only when assured resources are available (land, labour, capital and water).
A. Mixed cropping
Mixed cropping is growing of two or more crop simultaneously intermingled whith out any row pattern.
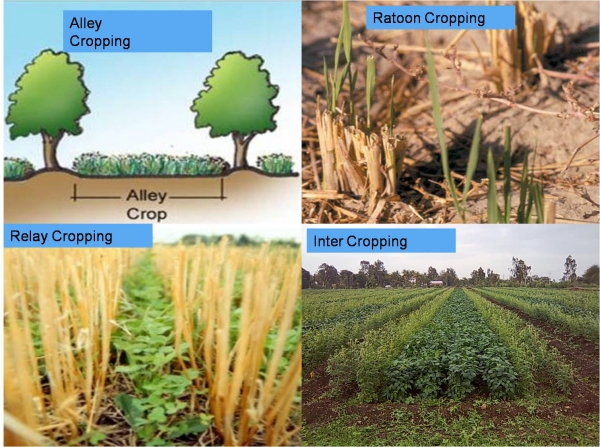
B. Intercropping
Intercropping is growing two more crops simultaneously on the same piece of land with a definite row pattern. For example, growing Sorghum + red gram in 3:1 ratio
C. Sequence Cropping / Crop rotation
It is a practice of growing two or more crops on the same piece of land during one farming year in particular sequence to increase the production without any detrimental effect on soil health. Depending on the number of crops grown in a year, it is called as double, triple and quadruple cropping involving two, three and four crops respectively.
D. Relay Cropping
Relay cropping refers to planting of the succeeding crop before harvesting the preceding crop. E.g. sowing of pigeon pea in-between two rows of kharif groundnut just one month before groundnut harvest. The main purpose is to utilise the residual soil moisture and nutrients after groundnut. This system also utilizes the solar energy efficiently.
E. Ratoon Cropping
Ratoon cropping or ratooning refers to raising a crop with regrowth coming out of roots or stalks after harvest of the crop. E.g. Raising a crop from regrowth of sugarcane, maize, sorghum etc.
F. Alley cropping
It is a practice of growing intercrops in the alleys formed by hedge row plants –perennial fodder.
• Ex: Subabul raised at 6 m row spacing
• The space between two rows called alleys.
• The intercrops are raised in the alley space.
• The intercrops raised in alleys are cotton, sorghum, blackgram
Cropping System

