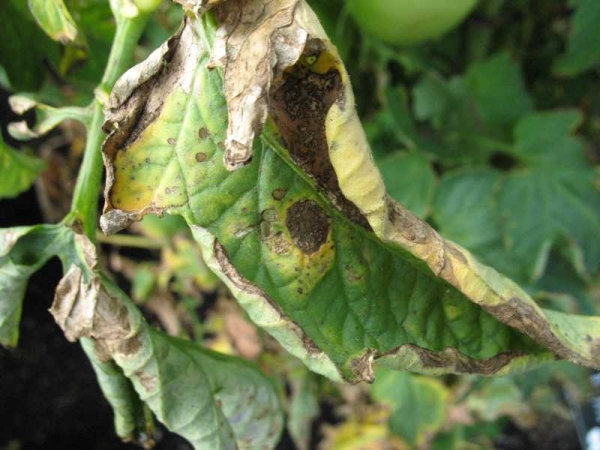

Early blight
Early blight1. Early blight:
-----------------------
C. O. Alternaria solani (Ell. and Mart) Jones and Grout
(Sub kingdom: Deuteromycotins; Order: moniliales; Family: Dematiaceae)
Symptoms:
• Irregular brown to dark brown spots of varying size appears on leaves
• Concentric lines inside the spot is distinct character
• Several spots coalesce to form larger patches, resulting leaf blighted
• Severe cases the entire foliage is blighted
Management:
• Grow resistant variety
• Spray mancozeb @ 0.25%
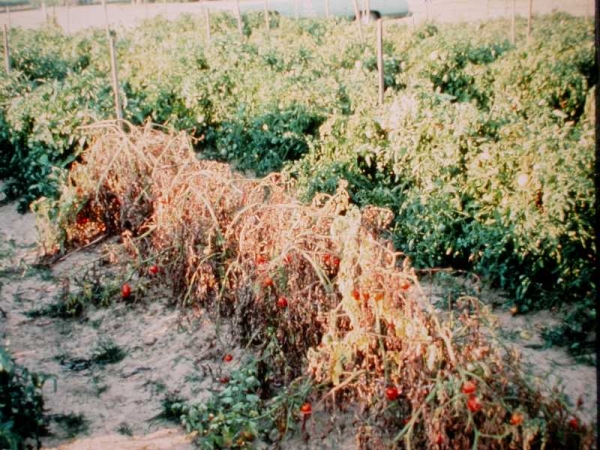

Fusarium wilt2. Fusarium wilt:
-------------------------
C O. Fusarium oxysporium f. lycopersici (Sacc.) Synder and Hansen
Symptoms:
• Initially clearing of the veinlet and chlorosis of the leaf and leaves droop and wilt
• Petiole and leaves droop and wilt
• In advanced stage, dark brown or black discoloration of the vascular tissues, a distinct character
Management:
• Grow resistant varieties viz. Rutgers, Marglobe, Pritchard, Kanora and Roma
• Avoid the monocropping, crop rotation with sorghum to be adopted
• Apply Trichoderma with FYM in the soil before sowing

Bacterial wilt
Bacterial wilt3. Bacterial wilt:
-------------------------
C. O. Burkholderia solanacearum
Symptoms:
• Dwarfing of the shoots with bronze discolorations of the leaves followed by wilting
• Vascular bundules become black and whitish bacterial ooze comes out of the cut ends of the stem
• The black streaks are apparent on stem
Management:
• Adopt various field sanitation measures at proper time
• Grow resistant varieties
• Crop rotation applied to avoid the tomato, potato, brinjal in the field for not less than two years.
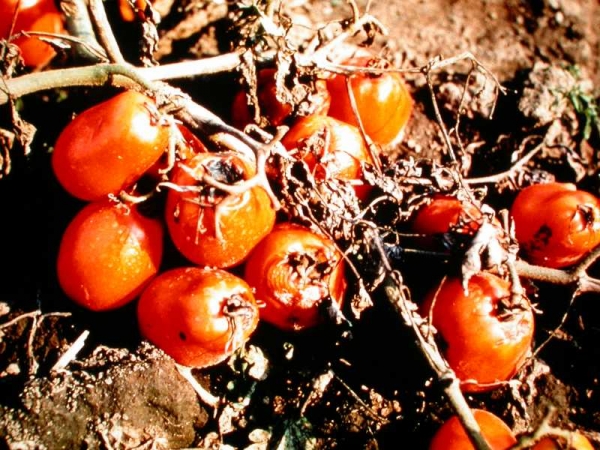

Fruit rot
Fruit rot4. Fruit rot:
----------------------
One of the severe disease, occurring during humid weather. Three species of Phytopthora i.e. P.infestans (Mont.) de Bary, P.palmivora Butl and P.parasitica Dast. Associated with fruit and/or stem rot. Besides Fusarium spp., Alternaria solani, Rhizopus sp. and Erwinia sp. are also associated with fruit rot in the field and in transit and storage. The damage caused varies considerably with the environmental conditions and handling in transit.

Stem and fruit canker
Fruit canker5. Stem and fruit canker:
---------------------------------
C. O. Clavibacter michiganense (E. F. Sm.) Davis et al.
Symptoms:
• Affects to the above ground plant parts
• Light brown streaks appear on the stem and leaf petioles, which turn black and cankerous
• Creamy bacterial ooze comes out from the affected stem and petiole
• On the fruit, water soaked lesions, with a white halo, later turning dark brown, corky and cankerous which may be deep seated and cover large portion
Management:
• Treat the seeds in 500 oppm of strepromycin solution
• Spray 500 ppm streptomycin 2-3 times at initiation of the disease on fruit
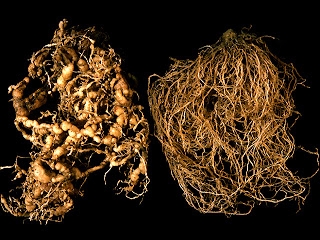
Root knot nematodes
Root knot nematodes6. Root knot nematodes:
------------------------------
C. O. Meloidogyne javanica (Treub.) Chitwood
Symptoms:
• Characterized by severe knotting of the roots
• Stunting of plant and poor fruiting
Management:
• Use disease free seedling for transplanting
• Use disease resistant variety
• Avoid the monocropping of solanaceus crops
• Apply carbofuran @ 33 kg/ha soil application during onset of infection

Viral diseases
Viral diseases Leaf curl7. Viral diseases:
-------------------------
a) Leaf curl
• Dwarfing, puckering and severe curling of the leaves
• Mottling, excessive branching, stunting and complete sterility of the plant
• Virus transmitted by the whitefly (Bemisia tabaci)
b) Spotted wilt
• Bronze marking on the upper surface of young leaves, extend from the leaf blade down to the petiole and stem
• Upward rolling of the leaves, yellow spotting on the fruits and final wilting
• Virus transmitted by thrips (Thrips tabaci)
c) Bushy stunt
• Severe stunting of the plant, the leaves and shoots are crowded and very much reduced in size
• Rarely flower and fruit, the stems are brittle, drop off and plant may wilt
Management:
• Rouging out the infected plant
• Spray systemic insecticides to manage the vectors of respective viral diseases

