Measurement of irrigation water
Units of measurement
• Water can be measured on
• Volume basis if it is at rest or on discharge basis if it is in motion. It is the volume of water passing through a section per unit time.
• Volume of water applied to a field can be suitably measured as ha-cm.
Methods of measuring water
Different methods - depend on the size of the stream and the available facility
(i) Volumetric method,
(ii) Velocity-area method in which velocity is measured by using float, current-meter etc.,
(iii) Measuring structures like weir, orifice, parshall flame etc.
Volumetric method
• Most simple and accurate method.Used to measure small discharge flowing through a channel or a pipe.
Float method
• Gives appropriate velocity - if no other means is available. Any object that flows in water but does not obstruct wind or get carried away by it, can be used as a float. A dry wood of about 1 cm3 size serves the purpose best. A straight section of the channel of about 30 meter length is selected such that the cross-section is almost uniform through the length. Several measurements are taken and the average time is noted. Average surface velocity = distance/time. The surface velocity is always higher than the average stream velocity. Therefore, the surface velocity is multiplied by a factor of 0.85 to get the average velocity.
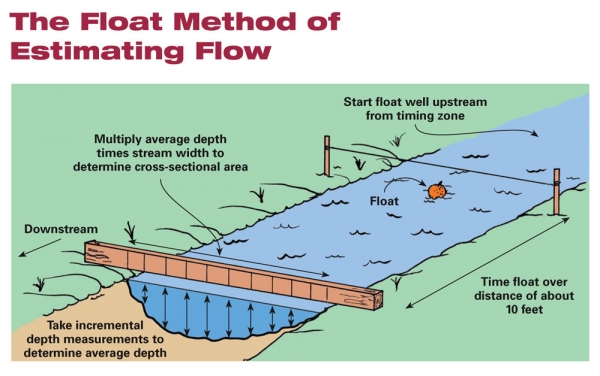
Float MethodCurrent meter method
• Cup type - consists of a wheel having several cups and Propeller type - vanes or propeller attached to a rod. When the meter is placed in flowing water, the velocity of water rotates the wheel or the vane. As the wheel rotates, the revolution is recorded in a counter. A calibration chart or a graph gives the relationship between the revolution per minute and the velocity. Shallow streams - current meter is suspended from a rod. In deep water - a cable is used to suspend the meter. Large rivers- boat is used to take readings inside the river. Current meter- suspended from a bridge if available. The average velocity is obtained by taking the average of the velocities at 0.8 and 0.2 of the depth from the top. In case of shallow stream, if it is not possible to take the reading at 0.8 of the depth from the surface, only one reading may be taken at 0.6 of the depth from the surface.
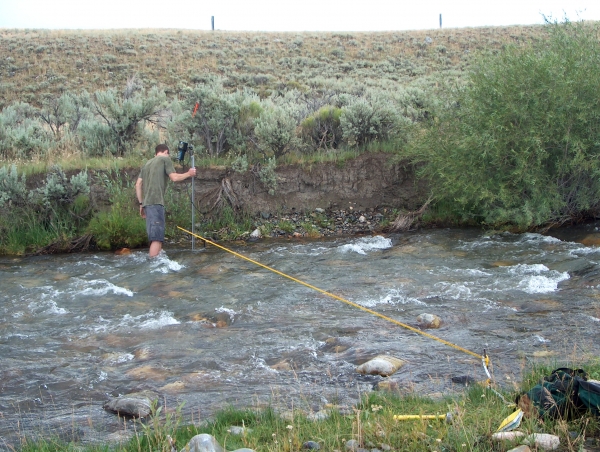

Velocity Measurement Using Current Meter
Current MeterWeirs
• A weir is a notch or opening of some definite shape installed on a channel or a stream through which water falls. Materials like wood, concrete, mild steel, rigid PVC etc. can be used for construction of a weir. Mainly a cut on a sheet metal is used for fabrication of weirs, to be installed at various locations in a channel.
Rectangular weir
• It is used to measure high discharge. Its crest is horizontal and the sides are vertical. In case, the crest length is same as that of the channel width, it is known as suppressed weir, otherwise contracted weir.
Trapezoidal weir
• It has a horizontal crest and the slides slope outward to give the notch a trapezoidal cross-section commonly a side slope of 1 horizontal to 4 vertical is used and it is named as Cipoletti weir. It does not require any correction for end contractions and is used for measurement of medium discharges. Normally it is a sharp crested weir. The formula for calculating discharge over a Cipoletti weir is Q = 0.0186 LH3/2.

Parshall Flume
Trapezoidal Weir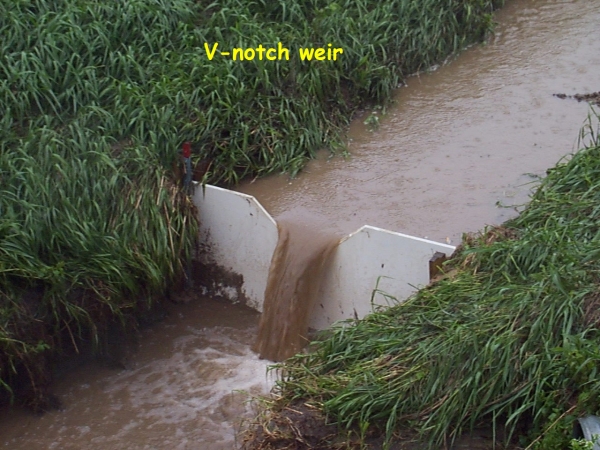
V-Notch WeirTriangular or V-notch weir
• It is used to measure small to medium discharges. The 90º V-notch weir is used to measure low discharges accurately. Thus the sides of the notch make an angle 45 º with the vertical which gives a slope of 1 horizontal to 1 vertical. In case of 90 º triangular weir, the discharge equation is Q = 0.0138 H5/2.

