What is meteorology?
Meteorology is defined as the science of atmosphere. It is a branch of atmospheric sciences of the earth dealing with physical processes in lower part of the atmosphere lying below about 35 km that produce weather.
Meteorology is concerned with the physical, chemical and dynamical state of the earth`s atmosphere and with the interaction between the earth`s atmosphere and the underlying surface. The word meteorology has been derived from the Greek words meteorologia from meteors means thing up above and logos mean study.
Aeronomy: Aeronomy may be defined as the study of upper part of the atmosphere (above about 35 km) where ionization and dissociation are important phenomena. It is a part of the atmospheric sciences.
The earth is a planet and the sun is a star. The earth is elliptical in shape. It has four spheres. They are:
1. Hydrosphere:- the water portion
2. Lithosphere: - the solid portion.
3. Atmosphere: - the gaseous portion.
4. Biosphere:-the living organisms/ life form - Plants & animals, man, M.O.
Meteorology is the physics of lower part of the atmosphere which results in the changes in the weather and climate at the surface of the earth. It is concerned with the physical, dynamic and chemical state of the earth`s atmosphere and with the interactions between the earth`s atmosphere and the underlying surface.
Weather and Climate:
Weather: Weather is defined as the physical state of atmosphere with respect to radiation, thermal, moisture and dynamic regime at a given place and at a given instant of time.
Climate: Climate represents a composite of the day to day weather conditions and of the atmospheric elements for a long period of time.
Elements of weather and climate
Climate and weather are expressed nearly by the same elements.
(1) Solar radiation (2) Temperature (3) Humidity (4) Pressure (5) Wind
(6) Precipitation (7) Evaporation
In case of weather, there are three additional elements namely, cloudiness, visibility and ceiling.
Climatic controls
The climate is influenced by several other factors. These factors are known as climatic controls. The physical, geographical, edaphic, physiographic and biotic parameters which interact with weather elements determine the climate of a place is called climatic controls.
Some of the important climatic controls are;
(1) Latitude (2) Altitude (3) Land and sea contrasts (4) Mountain barriers
(5) Local topography, ocean currents and (6) Vegetation or forest
(1) Latitude:
It is defined as the angular distance of a place from the equator and is expressed in degrees, minutes and seconds. It is a principal control of climate and determines the solar energy received and temperature of a place. Different types of climates according to latitude are equatorial, tropical, sub-tropical temperate and polar climates.
(2) Altitude:
It is defined as the height from mean sea level (MSL) and is expressed in meter. Temperature decreases with height. According to altitude there are two type of climate viz mountain climate and plateau climate.
(3) Water bodies and distance from sea: As the distance from sea of a place increases the difference between maximum and minimum temperature during a day and year increases. Depending on land and water bodies there are two types of climate such as maritime and continental climates. In maritime climate humidity is more and moderate temperature prevails. In continental climate the difference between maximum and minimum temperature is highest.
(4) Relief & mountain:
Mountains or hills interfere with wind flow controlling the temperature and rainfall wind ward side receives more rainfall while leeward side receives less rainfall and remains dry.
(5) Topography :
Undulation or unevenness of the surface changes the wind velocity which may change the temperature. Hence weather changes and fluctuations are more.
(6) Vegetation and Forest:
In forest climate due to evaportranspiration water vapour increases, humidity increases and temperature decreases. It also reduces incoming radiation and wind velocity.
Seasons
Earth appears to be stationary, but actually it is not . It has two types of motions: rotation and revolution. It spins on its axis at a speed of about 1600 km/ hour, making one complete rotation in about 23 hours, 56 minutes. The rotation of earth causes day and night. The second motion is around the sun in its orbit, which takes one year i.e. 365.25 days to complete, is known as one revolution. The average velocity of earth in its orbit is nearly 29.6 km/s. Due to revolution, different seasons occurs on the earth. The earth rotates on its axis from west to east (anti clockwise). The rotation of earth creates the coriolis force, due to which there is deflection of prevailing wind and ocean currents.
Perihelion and Aphelion
As the earth moves round the sun in an elliptical path, the distance between the sun and the earth vary with time. The earth is nearest to the sun during winter of northern Hemisphere. The distance between the sun and the earth is the least or lowest (147 * 106 km) on about January 3 on this day, the earth is known to be in Perihelion.
The distance between the sun and the earth is the farthest (152 * 106 km) on about July 4, on this day; the earth is known to be in Aphelion. The earth moves around the sun with greatest velocity at perihelion and the lowest velocity at aphelion.
(1) Spring season: March, April, And May: Vernal Equinox occurs on March- 21, Days and night are equal on that day on entire earth.
(2) Summer season: June, Jul, And Aug: Summer solstice occurs on June 21, long day and short night for northern hemisphere at same time inter solstice for the southern hemisphere.
(3) Autumn season Sept., Oct. and Nov.: Autumnal Equinox occurs on Sept. 23, Days and night are equal on that day on entire earth.
(4) Winter season: Dec., Jan., And Feb.: Winter solstice occurs on 22, long day, Short night
Importance of climate:
Climate influences all physical, chemical and biological activities over the earth.
It regulates the living conditions of plants and animals, their growth and development.
The living organisms have the ability to adjust themselves to the prevailing state of atmosphere to a certain extent, as the result of which special flora and fauna have developed in different climatic zones of the world.
Effect of climate in various spheres of human activities:
(1) Vegetation (2) Soils (3) Water resources (4) Agriculture (5) Forestry (6) Animal husbandry (7) Transportation and industry (8) Housing (9) Human comfort (10) Fishery
(1) Climate and Vegetation:
The direct influences of climate on plants are by precipitation, soil moisture, radiation, humidity, temperature, sunlight and wind. All species of vegetation have climatic requirements under which their growth is most efficient. Heat and moisture are great determiners of where plants will grow naturally and the energy and water budgets largely set the world pattern of vegetation.
(2) Climate and Soil formation:
Climate is an active natural factor influencing the formation of soils. Soils are affected by climate directly throughout their evolution from parent rock to disintegration (Physical break up) of parent rocks is induced climatically through rain splash, rainfall, snow hit, run off, glacier movements and wind etc.
(3) Climate and Water resources:
Of all the earth`s resources water is so fundamental to life. The availability of water at different times and places is ultimately related to weather and climate. The atmosphere is most active agent in the constant redistribution of water on earth`s surface. Hydrologic cycle of a region depends on the prevailing climatic situation of atmosphere.
(4) Climate and Agriculture:
The principal climatic factors affecting crop production are temperature, length of growing season, moisture conditions, sunlight and wind. Daily, seasonal or annual variations in any or all of the climatic elements are of importance in determining the efficiency of crop growth. The microclimate immediately around the plant is of vital significance.
(5) Climate and Forestry:
Now a day`s timber from forestry is also regarded as a crop and as such it is subjected to the influences of weather and climate just as field crops are. The relationship between climate and forests are reciprocal. The distribution and rate of growth of forest species are influenced by climatic conditions and on other hand forest affect the climate on a local scale.
(6) Climate and animal husbandry:
Domestic animals are highly dependent on the availability of feed. The climatic factor, which influences the growth of pastures or feed crops, exerts indirect influence on livestock. The suitability of a particular breed of animal to a climate depends on the quality and quantity of feed available. Climatic elements affect the livestock directly. The productivity of animals depend on climatic elements particularly temperatures.
(7) Climate transport and industry:
Weather and climate affect every economic activity viz. transportation, communication manufacturing and constructions. Application of meteorology and climatology for improvement of efficiencies in these fields require decisions at both the planning and operational stages. The climate is an important factor in long range planning, as in selection of factory site.
(8) Climate and Housing:
Atmospheric conditions are relevant factors in efficient setting, choice of materials, design, and air conditioning of the buildings other structures. Temperature, radiation, precipitation are chief elements requiring attention in proper designing of buildings.
(9) Climate & Human comfort:
Physiological functions of the human body respond to changes in weather. The incidence of certain disease varies with climate and the seasons. Type of food and clothing also reflect the climate and weather of a place. The state of atmosphere influences the mental and emotional outlook of human beings.
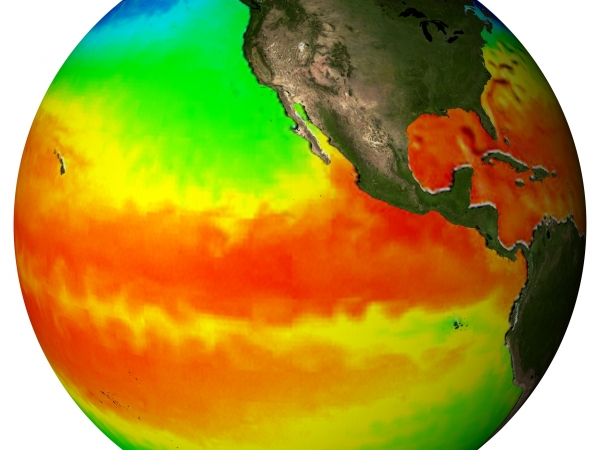
Earth temperature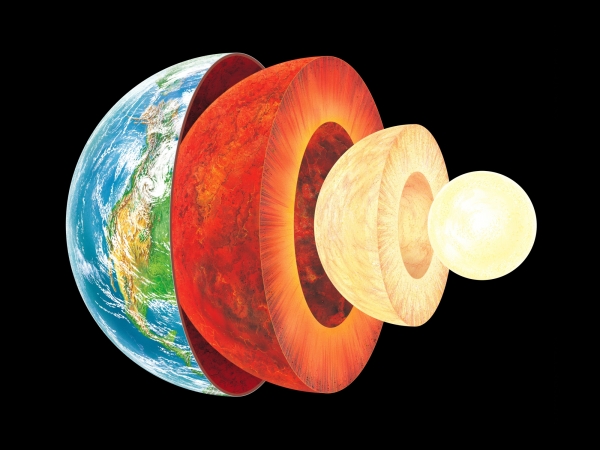
Earths layers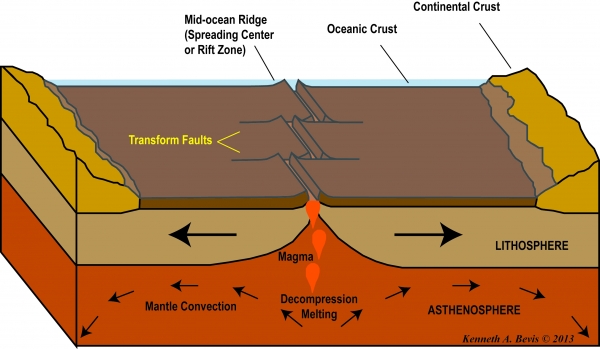
Physical geology
Ten indicators of global warming
Volcanic and Plutonic Igneous Rock Bodies
Weather symbols

