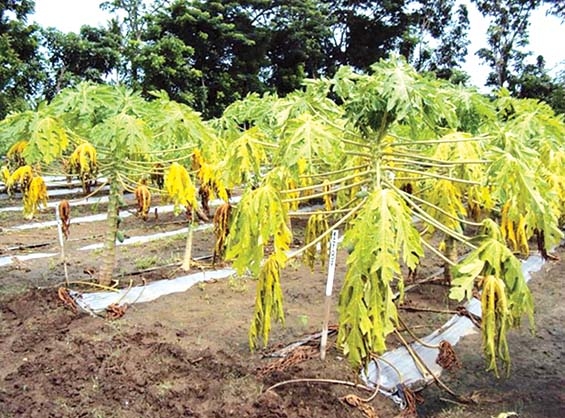

Stem rot/foot rotStem rot/foot rot:
--------------------
C.O.: Pythium aphanidermatum
Symptoms:
• Disease may lead to complete failure of crop when it appears in the early stages of growth.
• Water soaked patches appear on stem at ground level.
• These patches enlarge and girdle the base of stem.
• Diseased tissues of stem turn dark brown or black & red.
• Terminal leaves turn yellow, drop & wilt.
• Fruits shriveled and drop prematurely
• The entire plant topples over the ground.
• The internal tissues dry up and give a honeycomb appearance.
• Rotting may spread above and below on the stem and down to the roots.
• The roots deteriorate and may be destroyed.
Favorable condition:
• One week old seedlings are more susceptible. Stem rot caused by P. aphanidermatum is commonly noticed in 2 to 3 years old trees.
• The disease appears during rainy season and severity increase with the intensity of rainfall opt. temp. 36º C is favor47able for disease development.
Management:
• Selection of well drained field.
• Seed treatment captan or thiram or Chlorothalonil @ 4 g/kg .of seed
• Seedlings should be raised on well-drained nursery area.
• Diseased seedlings should be uprooted & destroyed.
• Drenching the tree basin with B. M.@ 1. % or captan @ 0.2 % or copper- oxycholoride @ 0.25 % or metalaxyl @ 0.1 % or tridemorph @ 0.1 % reduces the incidence of the disease.
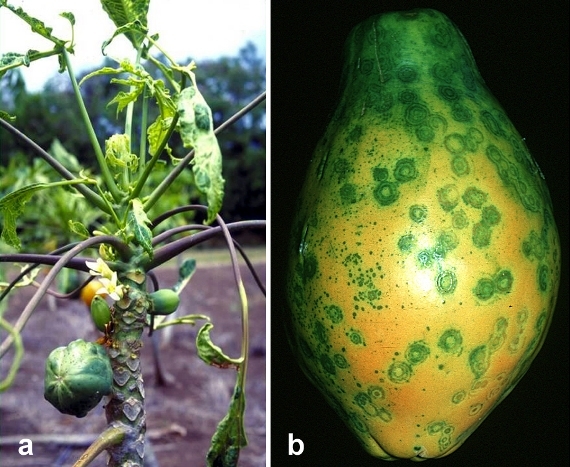
MosaicMosaic :
------------
C.O. Papaya Mosaic Virus (PaPMV)
Symptoms:
• Disease may appear at any stage of crop growth but most serious on young plants.
• Typical mosaic symptoms showing chlorosis with dark green blisters on leaves.
• Top young leaves of diseased plant are much reduced in size and show blister like patches of dark green tissue, alternating with yellowish green lamina and puckering.
• The leaf petiole is reduced in length and top leaves assume a upright position.
• On diseased fruits circular water soaked lesions with central solid spot appears.
• Fruits are deformed elongated and reduced in size and show mosaic patches.
• No reduction in the flow of latex.
Mode of spread and survival:
• The virus is transmitted by sap, grafting and several aphids – Aphis gossypii & Aphis medicaginis.
Management:
• Use healthy seedlings for planting.
• Roughing of infected plant & destroying them.
• Spraying of systemic insecticide for checking spread of vectors, monocrotophos @ 0.05 % or methyl-o- demeton @ 0.02 % .

Leaf curlLeaf curl:
------------
C.O.: Tobacco leaf curl virus (TLCV)
Symptoms:
• The disease is characterized by severe curling, crinkling and distortation of the leaves accompanied by vein clearing and reduction in leaf lamina.
• The leaf margins are rolled downward and inward in the form of inverted cap
• Veins thickened and turn dark green.
• Leaves become leathery and brittle and petioles are twisted
• Affected plants bear only a few flowers and fruits
• The plant become stunted and leaves get defoliated
Mode of spread:
• The disease is transmitted through white fly Bemisia tabaci .
Management:
• Infected plants should be destroyed from the nursery
• In orchard , the infected plants roughed and destroyed
• Spray trizophos or dimethoate 0.03% for controlling

