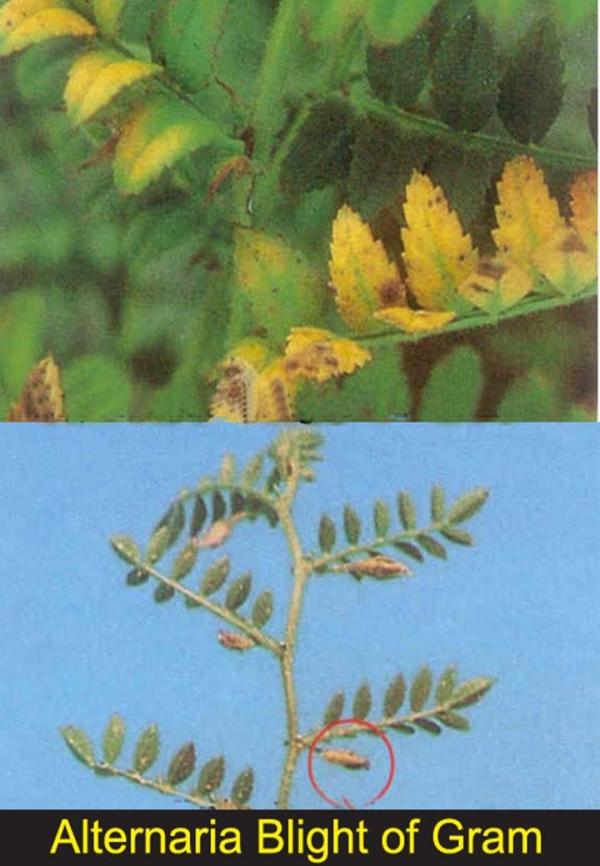

Alternaria blightAlternaria blight
--------------------
Symptoms
• The disease occurs during the flowering stage of the crop.
• Leaves are infected most.
• Shedding of lower leaves generally occurs in the infected plant.
• The lesions are seen on leaflets as water soaked, small, circular and purple in colour.
• Infected pods turn blackish in colour. Infected seeds get shriveled.
Control
• The plants should be planted distantly.
• Avoid excessive vegetative growth.
• Intercrop with linseed.
• Avoid excessive irrigation.
• Use mancozeb at the rate of 3g/l
OR
• Use Carbendazim at 1.5g/l.
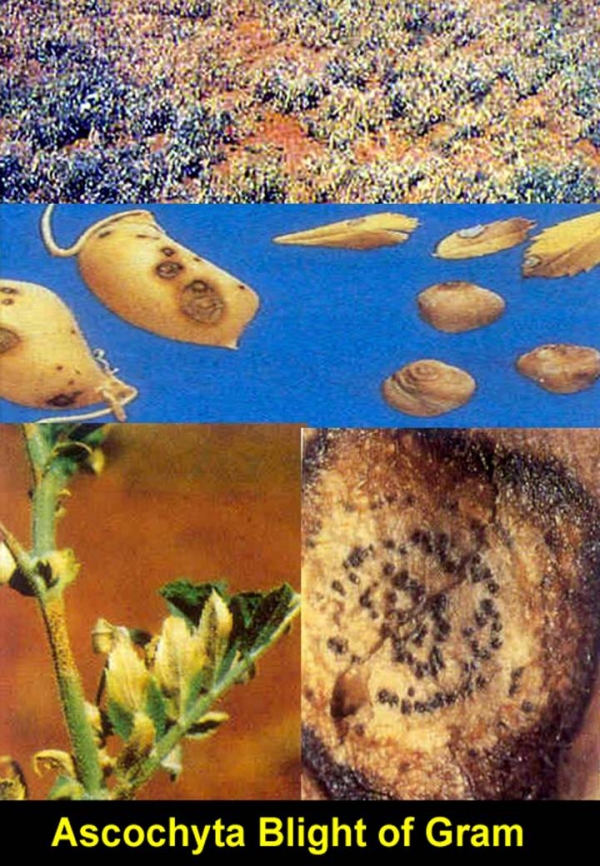

Ascochyta blight Ascochyta blight
-------------------
• This disease is caused by Ascochyta rabiei, a fungus which survives on plant trash left in the soil.
• All the plant part except the root is affected. Small round, yellowish-brown spots are seen on the leaves in the months of January and February.
• The spots also spread to petioles and branches where they are elongated and become dark brown in color.
• The affected plants finally dry up.
CONTROL MEASURES
1. Plant only healthy seed. Before planting treat the seed with fungicides like Thiram or Carbendazim (Bavistin) at the rate of 2.5 g/kg of seed.
2. Follow three year crop rotation.
3. Plant resistant varieties/tolerant varieties like G-543, Pusa-256, Gaurav, GNG-146, PBG-1 etc.

Fusarium wilt Fusarium wilt
---------------
• The main cause of this disease is a fungus, Fusarium oxysporum f.Sp. ciceri through other fungi are also associated with this disease.
• This disease causes considerable loss in most of the gram growing regions.
• The symptoms of the disease may be seen in the seedling stage as well as in an advanced stage of plant growth.
• The leaves start yellowing and afterwards drying.
• The plants too become yellowish and finally dry out.
• Roots turn black and ultimately decompose.
CONTROL MEASURES
• Seed Treatment with carbendazim at the rate of 2.5 gram per Kg. of seed.
OR
• Carboxin + Thiram 1:2 at the rate of 3 gram per Kg. Seed.
• Grow the resistant varieties like C-214, Avrodhi, Uday, BG-244; Pusa-362, JG-315, Phule G-5 etc.
• In fields having heavy incidence of gram wilt, the cultivation of chick pea should be avoided for three to four years.
• As far as possible sowing of chick pea should not be done before third week of October.
• Deep planting of chick pea about 8-10 centimeters deep in the light soils reduces the gram wilt incidence.
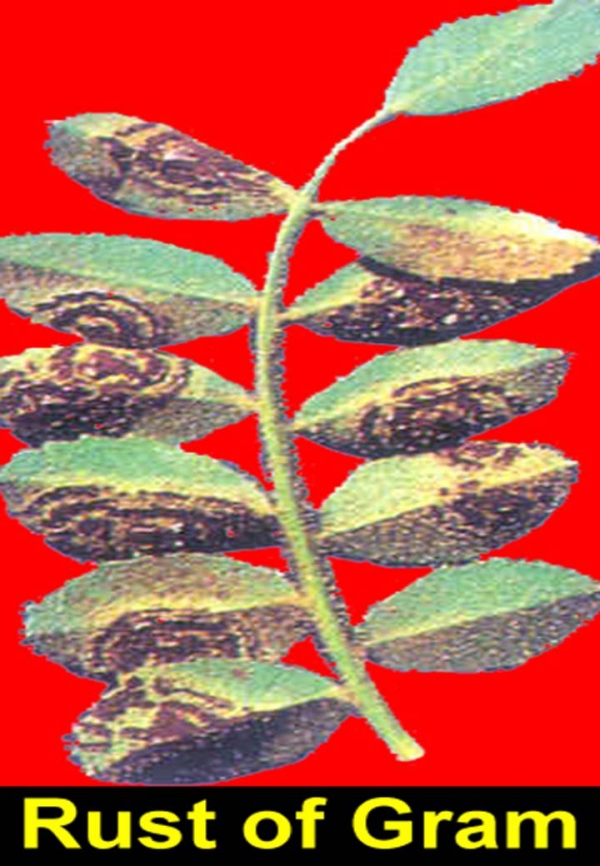

Rust Rust
------
• This disease is caused by a fungus Uromyces cicerarietini.
• The symptoms are visible in early February. Small, round to oval, light or dark brown pustules are formed on the under surface of the leaves.
• The pustules later turn black.
• Afterwards, these pustules appear on upper surface of leaves, petioles, twigs and pods.
• The affected leaves prematurely fall and therefore the yield is considerably reduced.
CONTROL MEASURES
• With the appearance of first symptoms, spray the crop with 0.2% Mancozeb 75 WP followed by two more sprays at 10 days interval.
• Plant only resistant varieties like Gaurav.
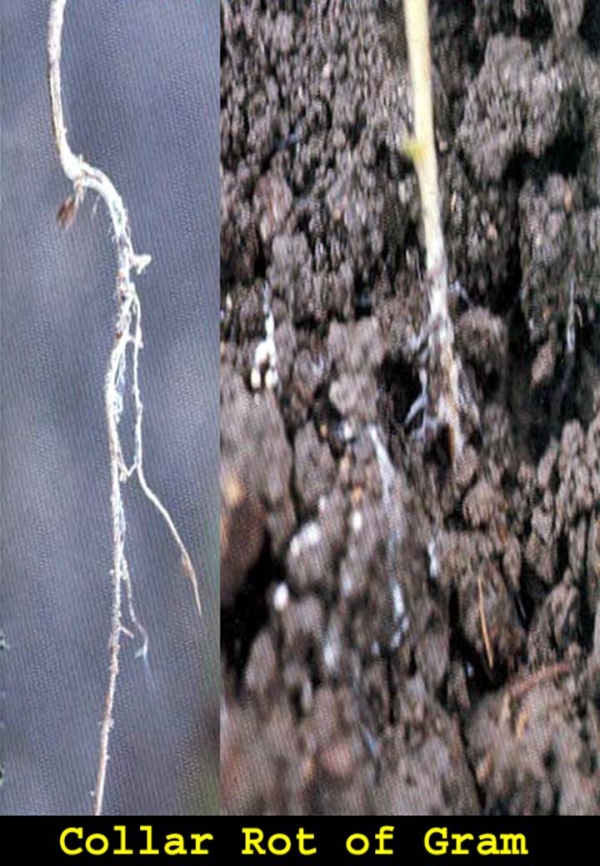

Collar rotCollar rot
------------
Sclerotium rolfsii
Symptoms
• It comes in the early stages i.e up to six weeks from sowing.
• Drying plants whose foliage turns slightly yellow before death, scattered in the field is an indication of the disease.
• Seedling becomes chlorotic.
• The joint of stem & root turns soft slightly contracts and begins to decay.
• Infected parts turn brown white.
• Black dots, like mustard in shape known as sclerotia are seen appearing on the white infected plant parts.
Control
• Deep pluoghing in summer.
• Avoid high moisture at the sowing time.
• Seedlings should be protected from excessive moisture.
• Destroy the residues of last crop and weed before sowing and after harvest.
• All un decomposed matter should be removed from the field before land preparation.
• Treat the seeds with a mixture of Carbendazim 1.5g and Thiram 1.5g per kg of seed.
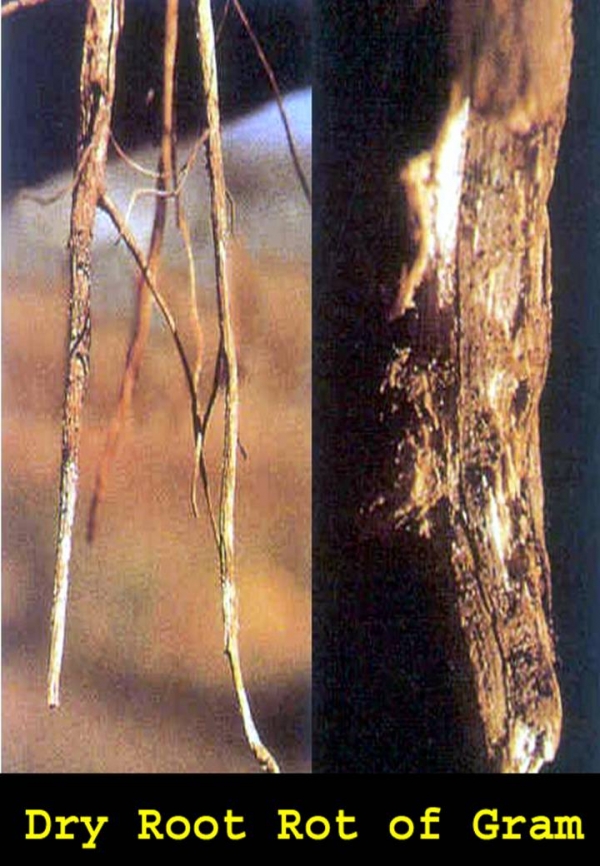
Dry root rotDry root rot
---------------
Rhizoctonia bataticola/Macrophomina phaseolina
Symptoms
• The disease appears from flowering to podding stage as scattered dried plants.
• The leaves and stem are become straw colored.
• Affected plants wither and spread across the entire field.
• The roots of infected plants become brittle and dry.
Control
• Deep ploughing in summer
• Grow cultivars resistant to dry root rot.
• Drought should be avoided.
• Sowing should always be done on the recommended time.
• Germinating and young seedlings should be saved from high temperatures.
• Seed treatment with a mixture of Carbendazim 1.5 g and Thiram 1.5 g per kg of seed.
OR
• Seed treatment with Trichoderma viride formulation + 3 g thiram per kg seed can reduce the disease incidence

Stemphylium blightStemphylium blight
----------------------
Stemphylium sarciniforme
Symptoms
• It infects the crop during the flowering stage.
• Defoliation or lower plant parts is common in infected plant.
• Lesions include ovoid spots which are dark brown in centre and have a grey border.
• Minute, dark brown, elongated spots also developed on the stems.
• The entire plant becomes black.
Control
• The crop should get maximum aeration and sunlight.
• Planting should be done distantly.
• Rouge out the infected plants.
• Gram should be intercropped with linseed.
• Spray of mancozeb at 3g/l or Carbendazim 1-1.5 g/L.

